This is a series of our course Basic Beliefs in Islam: This is part 3, Belief in Angels: Let’s see what is Muslim belief in Angels.
Table of Contents
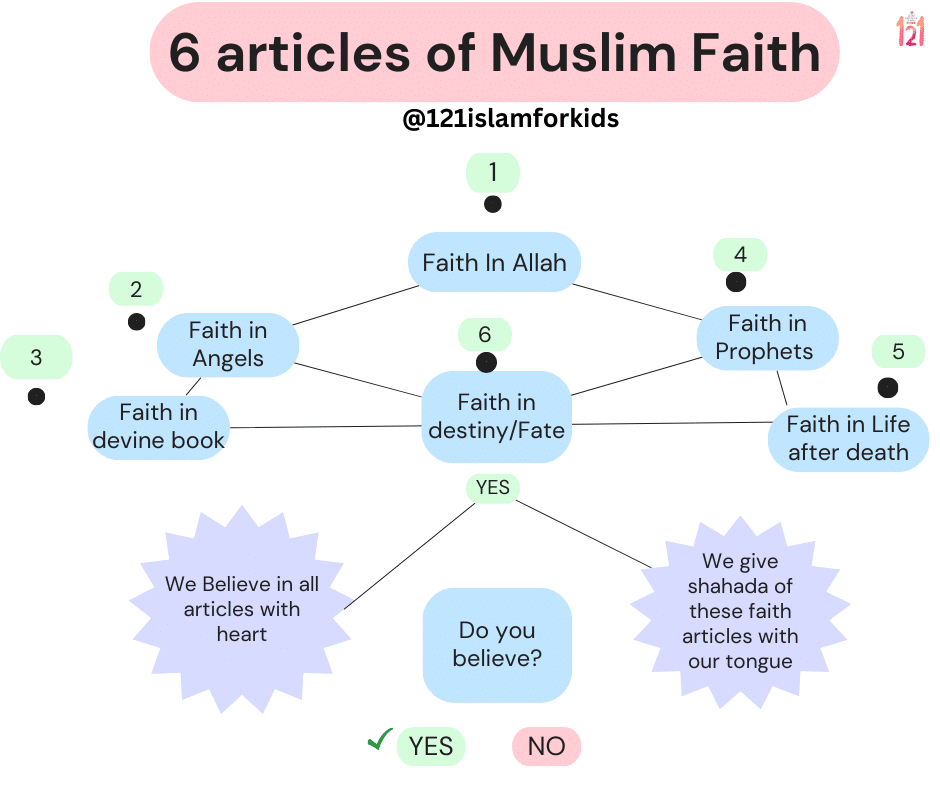
Basic beliefs in Islam: Belief in Angels Mind Map:
Main Topic: Islamic Belief in Angel
- Definition and Nature of Angels
- Created by Allah
- Spiritual beings made of light
- Subservient to Allah’s commands
- Invisible to humans
- Purpose and Role of Angels
- Worship and glorify Allah
- Carry out specific tasks assigned by Allah
- Messengers between Allah and His creation
- Belief in Specific Angels
- Jibril (Gabriel): Revelation and communication with prophets
- Mikail (Michael): Responsible for natural provisions and sustenance
- Israfil: Blowing the trumpet on the Day of Judgment
- Izrail (Azrael): Angel of death
- Raqib and Atid: Recording angels who document deeds
- Munkar and Nakir: Questioning Angels in the Grave
- Attributes and Characteristics of Angels
- Purity and obedience to Allah
- No free will or ability to disobey
- Unlimited knowledge and power
- Vast in number, beyond human comprehension
- Interactions with Humans
- Conveying messages from Allah to prophets
- Assisting and supporting believers
- Recording deeds and actions
- Intervening in human affairs with Allah’s permission
- Importance and Significance in Islam
- Affirming the unseen realm and the divine order
- Serving as a reminder of Allah’s power and presence
- Reinforcing the concept of accountability and divine justice
- Inspiring awe, reverence, and gratitude toward Allah
- References from the Quran and Hadith
- Quranic verses mentioning angels
- Hadiths narrated by the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) about angels
- Examples of angelic interventions and interactions in Islamic history
Conclusion: The Islamic belief in angels is a fundamental aspect of faith, affirming the unseen realm and the presence of Allah’s divine order. Angels play various roles, carrying out specific tasks assigned by Allah and serving as messengers between Allah and His creation. They possess unique attributes and characteristics, emphasizing their purity, obedience, and knowledge. Belief in angels reinforces accountability, divine justice, and the importance of a spiritual connection with Allah. References from the Quran and Hadith provide further evidence and guidance on the significance of angels in Islam.
Definition and Nature of Angels
Angels are special beings created by Allah from pure light. They obey Allah perfectly and have no choice but to follow His commands.
Angels are messengers between Allah and people. The angel Jibril (Gabriel) brought the Qur’an to Prophet Muhammad, and other angels have different jobs like protecting people and recording our deeds.
There are many angels, but we cannot count them. They watch over us, protect us, and help keep everything in the universe organized.
Muslims should respect and honor angels by making duaa (prayers). However, we should only worship Allah, not the angels.
Believing in angels is very important in Islam. The Qur’an and Hadith tell us many stories about angels and what they do.
Muslims confirm their belief in angels in various ways:
- We learn about angels from the Qur’an, which is Allah’s holy message.
- The Hadith (sayings of Prophet Muhammad) also tells us about angels and their jobs.
- Islamic teachers explain the stories about angels to help us understand them better.
- Some Muslims feel the protection and guidance of angels through their dreams and personal experiences.
- Our faith in Allah gives us faith in the angels He created to help us.
- We see Allah’s mercy, protection, and guidance in our lives, which angels help deliver.
- Muslims all over the world believe in angels, and this shared belief confirms it is true.
By understanding these beliefs, Muslims grow closer to Allah and appreciate His perfect plan.
Names of some angels and their role
- Archangels:
- Jibril (Gabriel): He is known as the angel of revelation and is responsible for delivering Allah’s messages to the prophets.
- Mikail (Michael): He is associated with the distribution of provisions and sustenance from Allah.
- Guardian Angels:
- Raqib and Atid: These angels are assigned to record the good and bad deeds of every individual.
- Recording Angels:
- Kiraman Katibin: They are a group of angels who record every action, word, and thought of humans. They write the deeds in a person’s book of records.
- Angel of Death:
- Izrail (Azrael): He is tasked with the responsibility of taking the souls of individuals at the time of their death.
- Angels of the Grave:
- Munkar and Nakir: These angels visit the deceased in their graves to question them about their faith and deeds.
- Angels of Mercy and Punishment:
- Ridwan: He is responsible for welcoming righteous believers into Paradise.
- Malik: He is in charge of Hellfire and overseeing its punishments.
- Angels of Protection:
- Muaqqibat: These angels are assigned to protect and accompany individuals, especially during critical moments.
Different types of angels have different roles and names mentioned in Islamic tradition. Each one has an important job in Allah’s creation.
Teaching Method Islamic Belief in Angels to Children:
Introduction:
- Start the lesson by introducing the topic of angels in Islam and their significance.
- Explain that angels are spiritual beings created by Allah and play an important role in the unseen world.
Definition and Nature of Angels:
- Teach children that angels are made of light and are subservient to Allah’s commands.
- Emphasize that angels are invisible to humans and exist in a realm beyond our perception.
Purpose and Role of Angels:
- Discuss the purpose of angels, which is to worship and glorify Allah.
- Explain that angels also carry out specific tasks assigned by Allah, such as delivering messages to prophets.
Belief in Specific Angels:
- Introduce some prominent angels in Islam, such as Jibril (Gabriel), Mikail (Michael), Israfil, and Izrail (Azrael).
- Explain their roles and responsibilities, making the concepts relatable to children.
- Share stories from Islamic history that involve these angels to engage children’s interest.
Attributes and Characteristics of Angels:
- Discuss the qualities of angels, such as their purity, obedience to Allah, and vast knowledge.
- Explain that angels do not have free will or the ability to disobey Allah.
- Highlighting their power and vast numbers, which are beyond human comprehension.
Interactions with Humans:
- Explain that angels serve as messengers between Allah and His creation.
- Discuss how angels deliver revelations to prophets, such as Jibril conveying the Quran to Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him).
- Teach children that angels record their deeds and actions, and will be present during the questioning in the grave.
Importance and Significance in Islam:
- Emphasize the importance of believing in angels as part of faith in Islam.
- Explain that belief in angels affirms the unseen realm and the divine order established by Allah.
- Discuss how angels remind us of Allah’s power, presence, and the concept of accountability.
References from the Quran and Hadith:
Different angels have different jobs. Some bring messages from Allah to the prophets, some record what we do, and some manage the weather. Each angel’s job is important and helps keep everything in the universe working perfectly.
Duties of Angels in Islam
We don’t know exactly how many angels exist. Allah created so many angels that no human can count them. Each person has angels with them to protect and watch over them.
How Many Angels are There in Islam?
Yes! Believing in angels is a very important part of being Muslim. The Qur’an and Hadith teach us that angels are real and they help Allah’s creation in many ways.
Do Muslims Believe in Angels?
- Share selected Quranic verses mentioning angels, such as Surah Al-Baqarah (2:97) and Surah Al-Anbiya (21:27).
- Narrate age-appropriate hadiths from the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) about angels and their interactions.
- Relate examples from Islamic history where angels played significant roles, such as the Angel Jibril appearing to Maryam (Mary).
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key points covered in the lesson, emphasizing the belief in angels as an integral part of the Islamic faith.
- Encourage children to reflect on the importance of angels in their lives and to appreciate Allah’s creation.
- Remind them that belief in angels strengthens their connection with Allah and reinforces the concept of accountability.
When teaching children about angels, use simple words, stories, and fun activities. This helps them understand and love learning about the unseen world and Allah’s perfect creation.
This article is a series of our 6 articles in Islam course. Other articles on this course.